With new IoT devices and sensors entering the market there is an increasing demand for gateways that can connect these devices to the internet. Helium network is a new network that uses blockchain technology to incentivize people to install LoRaWAN Gateways which through the LoRa technology can receive and transmit data for sensors and other IoT devices nearby. The helium network and its cryptocurrency are based on a new approach to finding crypto the so-called proof of coverage. This means that the Gateways and Hotspots produce helium coins depending on the area they cover. In this post, we will show you the coverage we achieved with the new SenseCAP M1 and give you some tips on how to get the most out of the SenseCAP M1. In our tests, we used two different bandwidths that are the standard in America (915Mhz) and Europe(868Mhz).
Range with different antennas
The specifications for the devices used in our tests are:
915MHz Sensornode: POWER: 22 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 21
915MHz Gateway: POWER: 27 dB ,BW: 500KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 22
868MHz Sensornode: POWER: 22 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 21
868MHz Gateway: POWER: 27 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 22
We installed the SenseCAP M1 Gateway in our office on the 10th floor in the center of Shenzhen. Then we installed Sensor nodes at different locations and tested the performance by sending packages between the Sensor nodes and gateway to see how many packages come through, the received signal strength(RSSI), and the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)


First Scenario:
At the first test the sensor node was placed in a school at a distance of approximately 1.6km (1 mile).
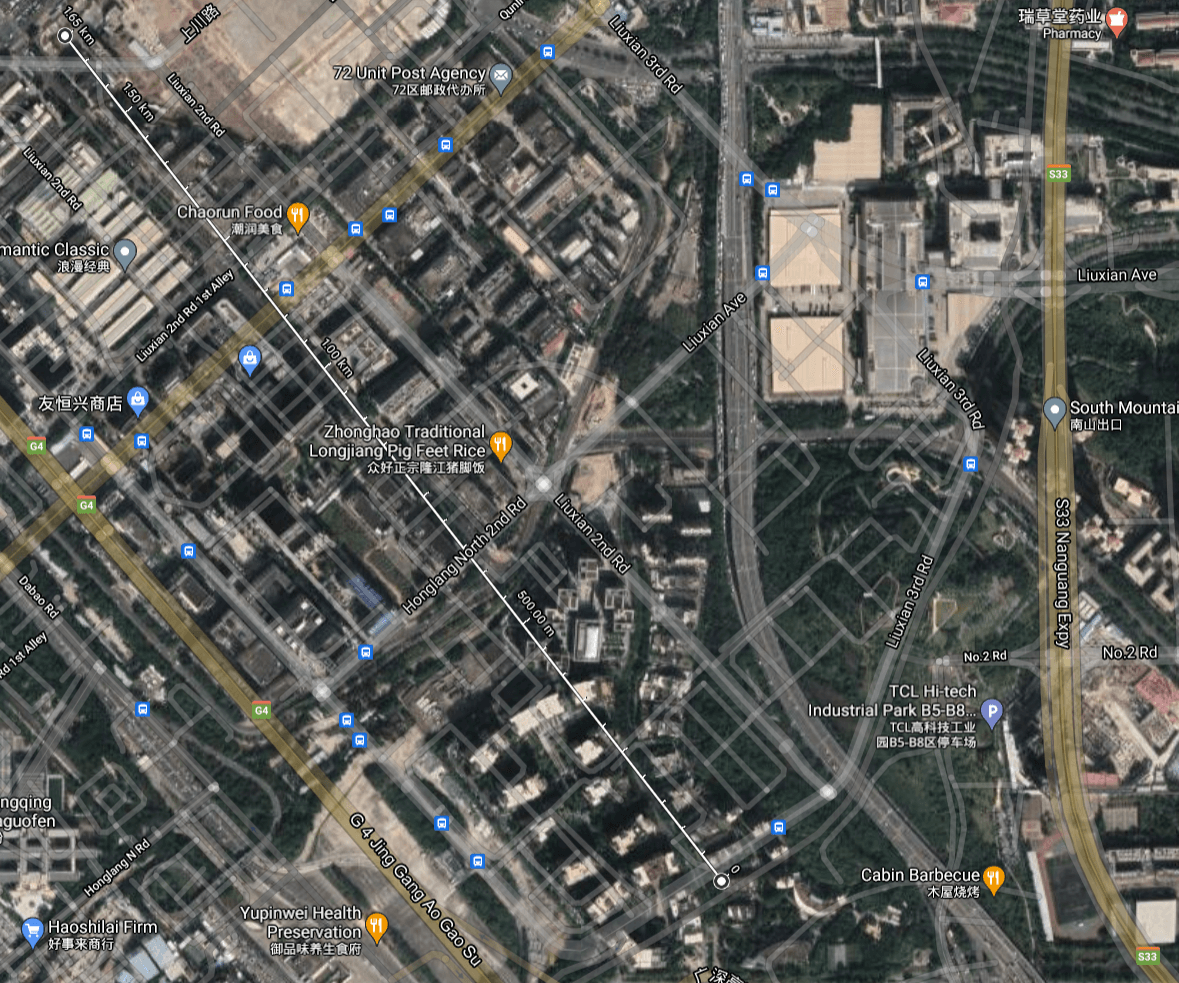
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 915-Node to Gateway | 95% | -81.9 | 8.8 |
| 915-Gateway to Node | 88% | -76 | -17 |
| 868-Node to Gateway | 100 | -98 | 1.2 |
| 868-Gateway to node | 98% | -83 | 4 |
*915 experiences Interference
Second Scenario
For this scenario, the Sensor node is employed on a rooftop 1.4km (0.87 miles) away.
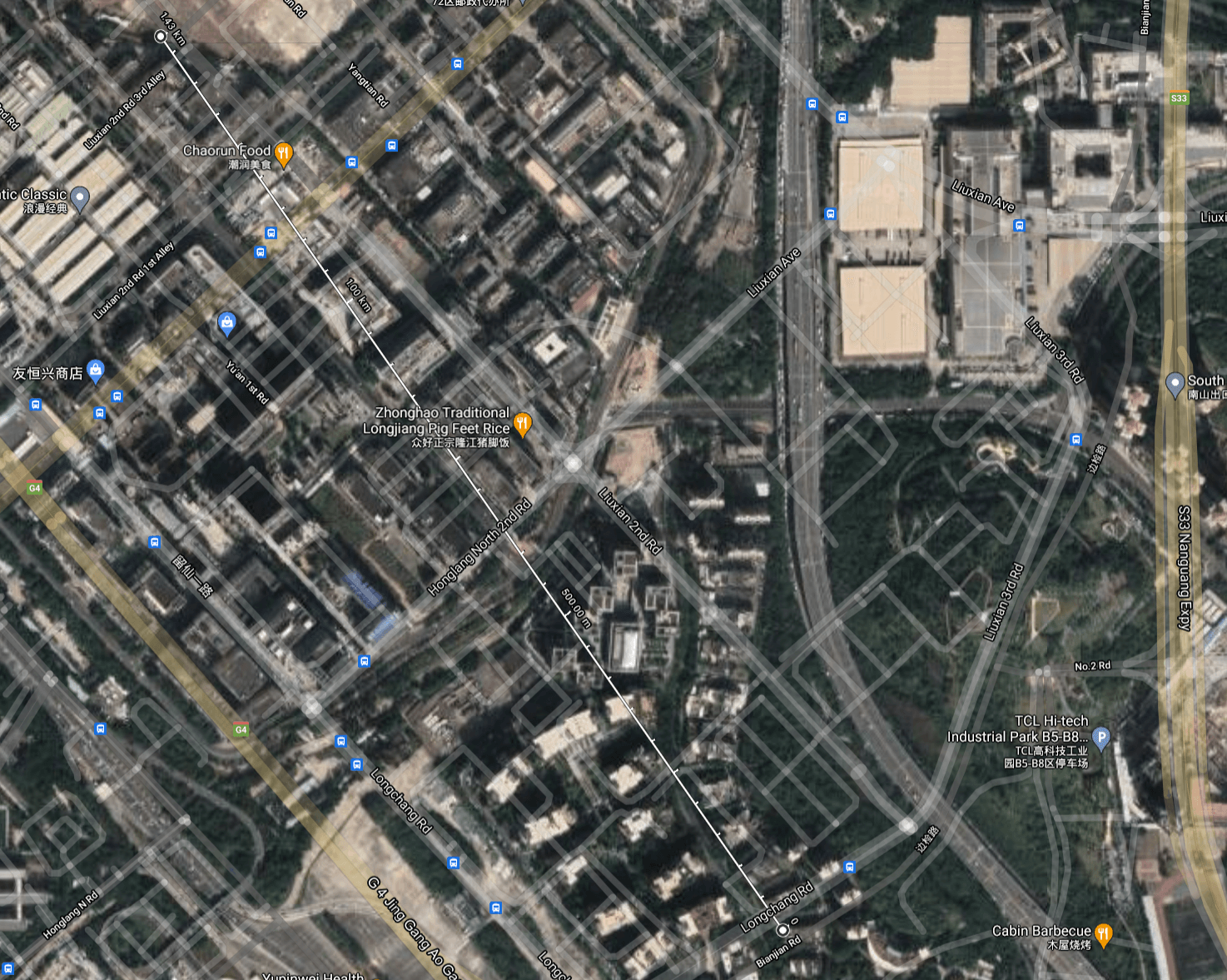
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 915-Node to Gateway | 99% | -86.8 | +5.0 |
| 915-Gateway to Node | 97% | -74 | -12 |
| 868-Node to Gateway | 97% | -93.9 | 4.2 |
| 868-Gateway to node | 96% | -71 | -14 |
*915 and 868 both experience interference.
Third Scenario
The sensor node is 1.1km(0.68miles) from the gateway and is set up next to a busy subway station.
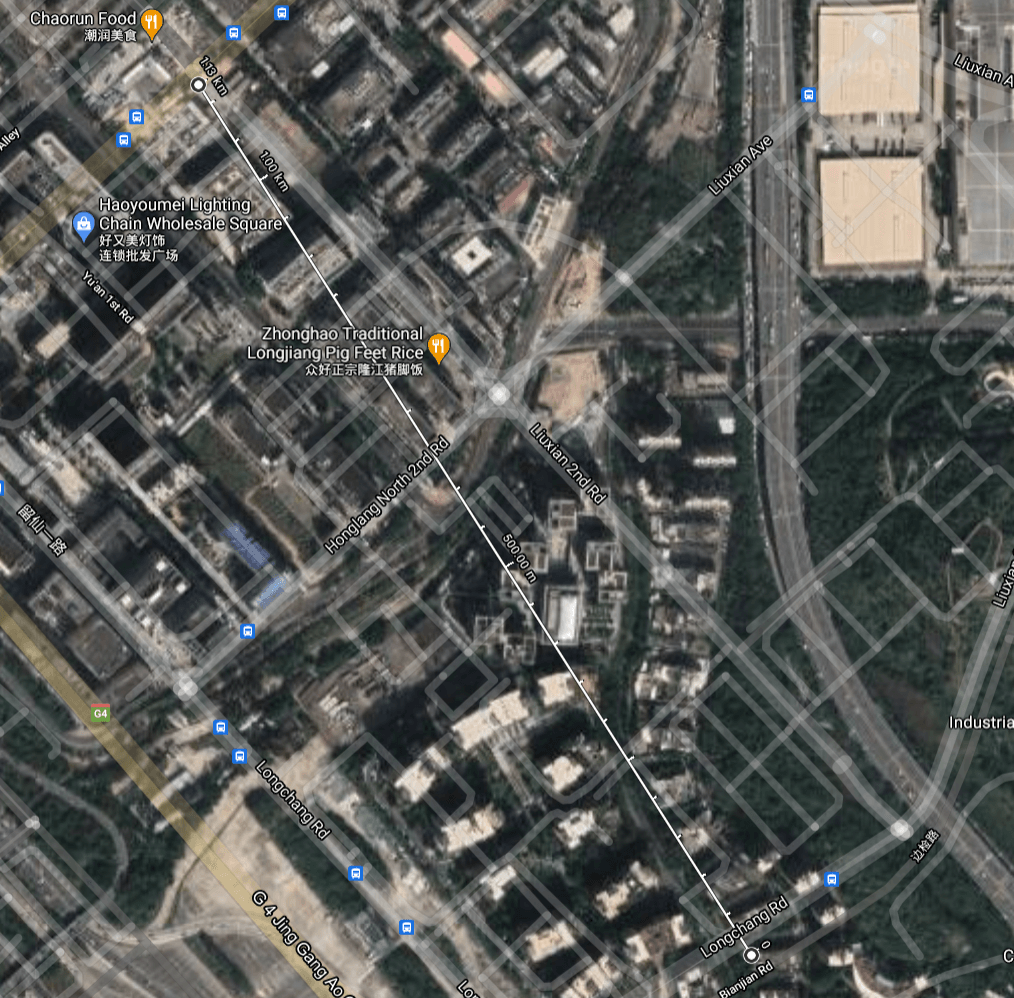
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 915-Node to Gateway | 100% | -89.8 | +3.5 |
| 915-Gateway to Node | 100% | -76 | 3 |
| 868-Node to Gateway | 100% | -94.8 | +3.8 |
| 868-Gateway to node | 100% | -81 | -4 |
Conclusion:
For our first tests, the results were from acceptable to excellent. Except for the 915 Gateway to Node test for the first scenario, the package delivery rate was above 95% and in the last scene it reached 100% for all 4 tests. In all our tests the RSSI comfortably exceeded
-120dBm which is considered the RSSI minimum for LoRa Networks. While there is interference in scenarios two and three the SNR values are still between -20dB and 10dB which is the typical bounds LoRa SNR values.
Note: The signal strength of 915 and 868 in the third round of testing is similar to the signal strength of the previous E5 and SX1301 1KM stretch tests.
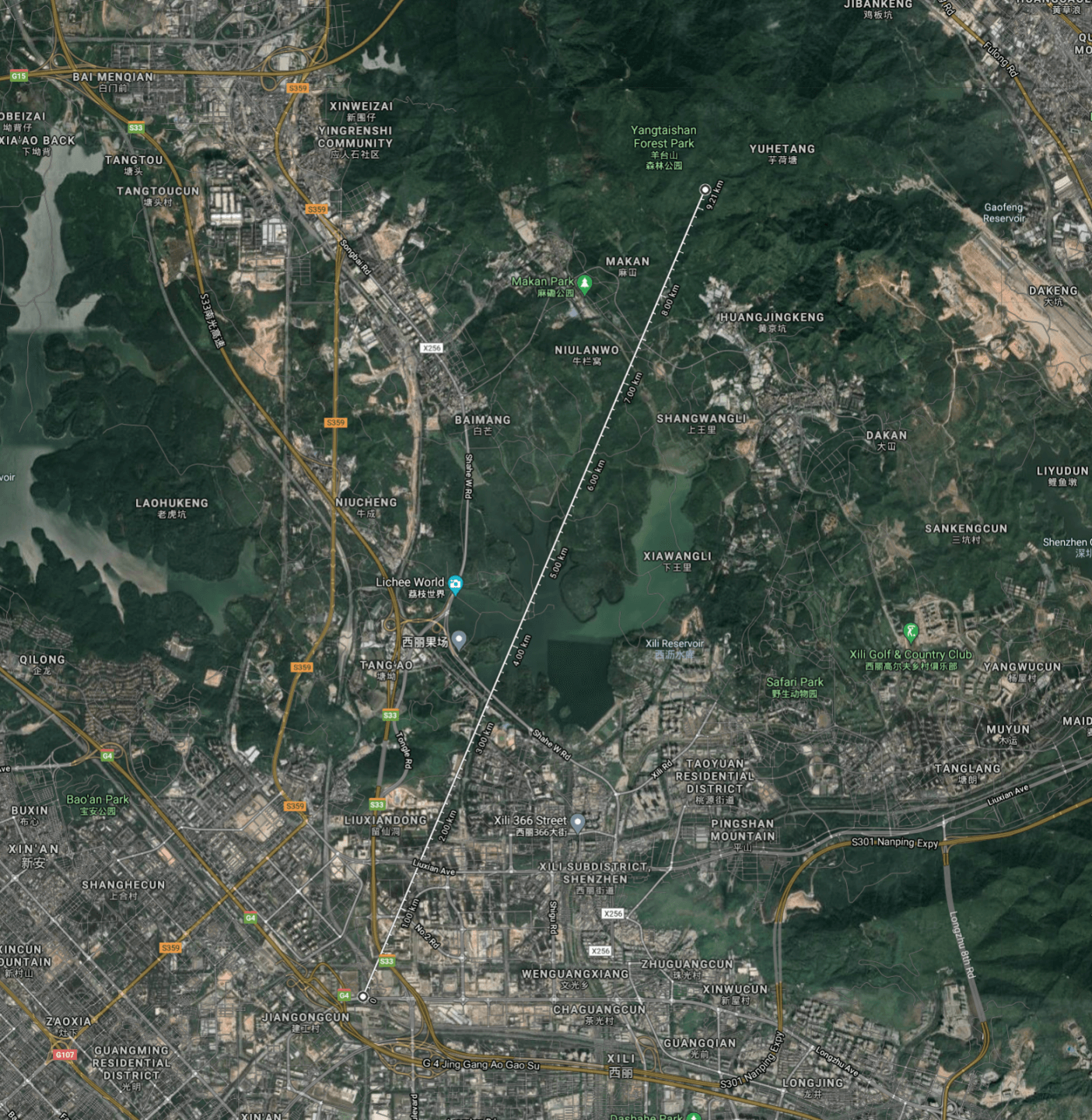
SX1302 Mountain Distance Test-05-29
M1 gateway (915+868): the top of the G2 building,
Node E5: Yang Tai Mountain
In the next tests, we will try to push the range of our SenseCAP M1 LoRaWAN gateway to the limit and see the maximum distance over which we can still successfully transmit data. Like in the scene before we deploy our Gateway on the 10th floor of our office building. Then we deploy a node with the LoRa E5 module on a mountain at a nearby park. For this test, the distance between the Sensor node and the Gateway was 9.2km (5.7 miles). The node and gateway were sending 100 packages back and forth and we tested the connection with different types of antennae.
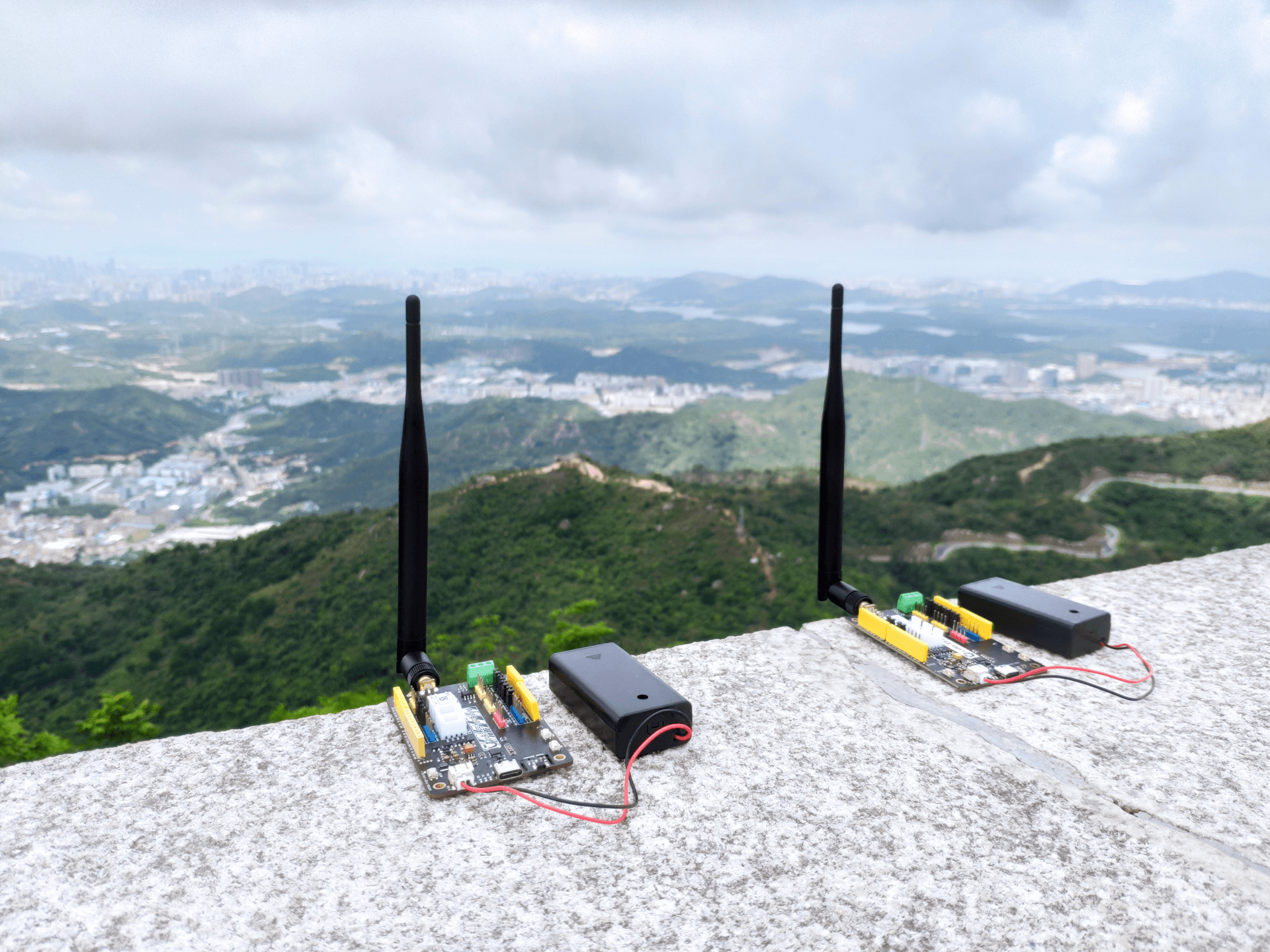

Node and gateway parameters
915 node: POWER: 22 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 21
915 GW: POWER: 27 dB, BW: 500KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 22
868 node: POWER: 22 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 21
868 GW: POWER: 27 dB. BW: 125KHZ, SF: 12, CR: 4/5, size: 22
In the first round, we added a 7db Fiberglass antenna to the 915 Gateway and an 8db Fiberglass antenna to the 868 Gateway
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 915 Node | 100% | -75 | 2 |
| 915 Gateway | 100% | -91 | 2 |
| 868 Node | 100% | -76 | -1 |
| 868 Gateway | 100% | -88 | 0 |
The second round of testing consists of the 868 Gateway together with a 5db Fibreglass antenna:
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 868 Node | 100% | -78 | 3 |
| 868 Gateway | 100% | -90 | 0 |
In the third and final round we were testing the antennas that come with devices.
| Packages delivered | RSSI | SNR | |
| 915 Node | 100% | -81 | 4 |
| 915 Gateway | 100% | -91 | 2 |
| 868 Node | 100% | -80 | 2 |
| 868 Gateway | 100% | -92 | 2 |
Conclusion:
Both the 868 and the 915-version performed excellently in our field test. All 3 antenna setups had a transmission rate of a 100%. While the fiberglass antennas might be useful in certain application scenarios where the gateway cannot be mounted at a convenient location the last test showed that in many cases an antenna is not necessary and that the basic antenna performed very well. Again all the values for RSSI were above the threshold of -120dBm and there was less interference than in the previous test.
To conclude the results of our tests, if you purchase a new helium hotspot you do not necessarily need to buy the strongest and most powerful antenna but should instead pay attention to the location of your new device (or at least the antenna). The most important aspects in choosing the placement for your new hotspot are the view and height. A good view means that your antenna is not blocked by walls, trees, or other obstacles and has a clear view on the surrounding area. The other important parameter is height. According to the American Radio Relay League, “a transmitting antenna at 120 feet [37 meters] will provide the effect of approximately 8 to 10 times more transmitting power than the same antenna at 35 feet[11meter]” So you should try to mount your device and antenna as high as possible. A rule of thumb says you can reach around 90% of optimum earnings if your antenna is at least 6 meters (20 feet) above your own roof and all the surrounding roofs or obstacles.
So we hope this post can give you a better idea of how to maximize your earnings with a new hotspot. Contact the … to get our new SenseCAP M1 indoor LoRaWAN Helium Hotspot